What Is SKU? SKU Meaning In Sales & Manufacturing


Table of Contents
- What Is SKU and Why Is It Important in Sales and Manufacturing?
- Key Differences Between SKU and Universal Product Code (UPC)
- Implementing an Effective SKU System in Your Sales and Manufacturing Processes
- The No. 1 Tool for all dropshippers – now with AI
- Examples of Effective SKU Utilization in Different Industries
- The Future of SKU Management: Leveraging Automation and AI
- Conclusion
What Is SKU and Why Is It Important in Sales and Manufacturing?
SKU, or Stock Keeping Unit, is a unique identifier for each product within a company’s inventory. But, what exactly is the SKU meaning? Let’s find out!
It’s a critical tool for managing stock levels, tracking items across multiple locations, and aiding in sales analysis.
But let’s dive deeper into the SKU meaning and its significance.
The Functionality of SKUs in Sales and Inventory Tracking

Imagine an e-commerce business that sells an array of products online.
Each item has distinct characteristics such as size, color, and style. SKUs come into play by providing a shorthand for this detailed information, making it easier to track and manage inventory.
This systemization is not just about keeping things neat; it’s about enabling efficient operations from the warehouse to the customer’s doorstep.
➡ Efficiency in E-commerce
In e-commerce businesses, where orders are received around the clock, SKUs are indispensable.
They allow for quick identification of products during order fulfillment. With a well-implemented SKU system, businesses can swiftly process orders, ensuring customers receive their purchases without delay.
➡ Product Tracking
Each SKU corresponds to specific product information, which means every movement of an item within the inventory can be monitored. This aids not only in maintaining optimal stock levels but also in understanding sales trends for each product.
➡ Preventing Overstocking or Stockouts
By using SKUs to observe product movement patterns, companies can predict future sales with greater accuracy.
This predictive power enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding restocking, reducing the risk of overstocking which ties up capital or stockouts that lead to lost sales.
The importance of SKU in sales and manufacturing cannot be overstated.
In a high-paced sales environment, tracking every single item manually is impractical and prone to errors.
SKUs automate this process, allowing businesses to concentrate on growth rather than getting bogged down by inventory management woes.
So, by leveraging SKUs:
- Sales Analysis becomes streamlined as sellers can pinpoint which products are performing well.
- Inventory Management turns into a data-driven strategy rather than guesswork.
- Customer Satisfaction improves due to faster order processing and accurate fulfillment.
In essence, SKUs act as the lifeblood of inventory systems within the vast ecosystem of sales and manufacturing.
Thus, they provide critical insight into product lifecycles—information that savvy business owners use to stay competitive in a bustling market landscape.
Whether you’re running a small shop online or managing a complex manufacturing chain, mastering your SKU system sets you apart and propels you toward efficiency and success.
Advantages of Implementing a Robust SKU System for Demand Forecasting and Reorder Management
Understanding what the SKU meaning and why it’s important can bring many advantages to any business.
SKUs, or Stock Keeping Units, are unique codes assigned to products in inventory management.
Here’s why SKUs are essential for sales and manufacturing:
✅ Optimizing Inventory Holding Costs
One of the main goals for businesses is to find the right balance between having too much or too little stock. A well-designed SKU system can help achieve this by providing detailed information on how each product moves in and out of inventory.
With this data, businesses can make better decisions about managing their stock, resulting in lower holding costs.
✅ Meeting Customer Demand Effectively
A strong SKU system allows businesses to analyze sales patterns and customer buying behavior accurately.
This knowledge is crucial in predicting future demand and making sure that the right products are available when customers want them.
By doing so, businesses can meet customer demand effectively and improve satisfaction.
✅ Setting Reorder Points Based on Historical Sales Data and Lead Times
SKUs are also useful for determining when to reorder products.
By studying past sales data and lead times for each SKU, businesses can identify at what stock level they should place new orders.
This proactive approach helps prevent situations where stock runs out or there’s too much inventory on hand.
Inventory management is crucial for any business, whether it’s involved in sales or manufacturing.
However, SKUs have benefits that go beyond just managing inventory – they also play a role in Customer Service and Fulfillment Processes.
In the next sections, we’ll explore how SKUs streamline these areas of operations.
Ensuring Seamless Operations: SKU’s Role in Streamlining Customer Service and Fulfillment Processes
SKU, short for Stock Keeping Unit, is more than just a series of alphanumeric identifiers for items in inventory.
It’s the lifeblood of order management systems, playing a pivotal role across sales and manufacturing landscapes.
So, let’s break down the significance of SKU meaning and how it facilitates an array of processes:
1. Accurate SKU Information: The Backbone of Customer Service
Accurate SKU data ensures that customer service representatives have immediate access to product information.
Hence, this speed is essential when providing timely order updates or resolving customer queries, which in turn boosts customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Product Tracking and Sales Analysis: A Deeper Look
By using SKUs, businesses can track products throughout their lifecycle, from procurement to sale.
This detailed product tracking enables comprehensive sales analysis, leading to informed business decisions and strategies.
3. Picking, Packing, and Shipping: Efficiency in Action
SKUs are instrumental during the picking and packing stages in warehouses. Workers can quickly locate items due to clear SKU labeling, reducing the time spent on each order. When it comes to shipping, SKUs assist in verifying that the correct product is sent out, thereby minimizing errors and returns.
4. The Importance of SKU in Sales and Manufacturing: A Dual Advantage
In both sales and manufacturing realms, the importance of SKU meaning cannot be overstated.
It’s not just about keeping tabs on inventory; it’s about creating a seamless flow from shelf to shipment.
So, here’s why SKUs are crucial:
- They provide a quick reference for inventory levels, ensuring that popular items are always stocked.
- SKUs simplify the process of returns or exchanges by allowing for easy identification of items.
- They help maintain consistency across different channels and store locations.
By integrating SKUs into customer service protocols and fulfillment operations, businesses experience fewer hiccups and enjoy smoother operations.
This level of organization is key for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced market.
Key Differences Between SKU and Universal Product Code (UPC)
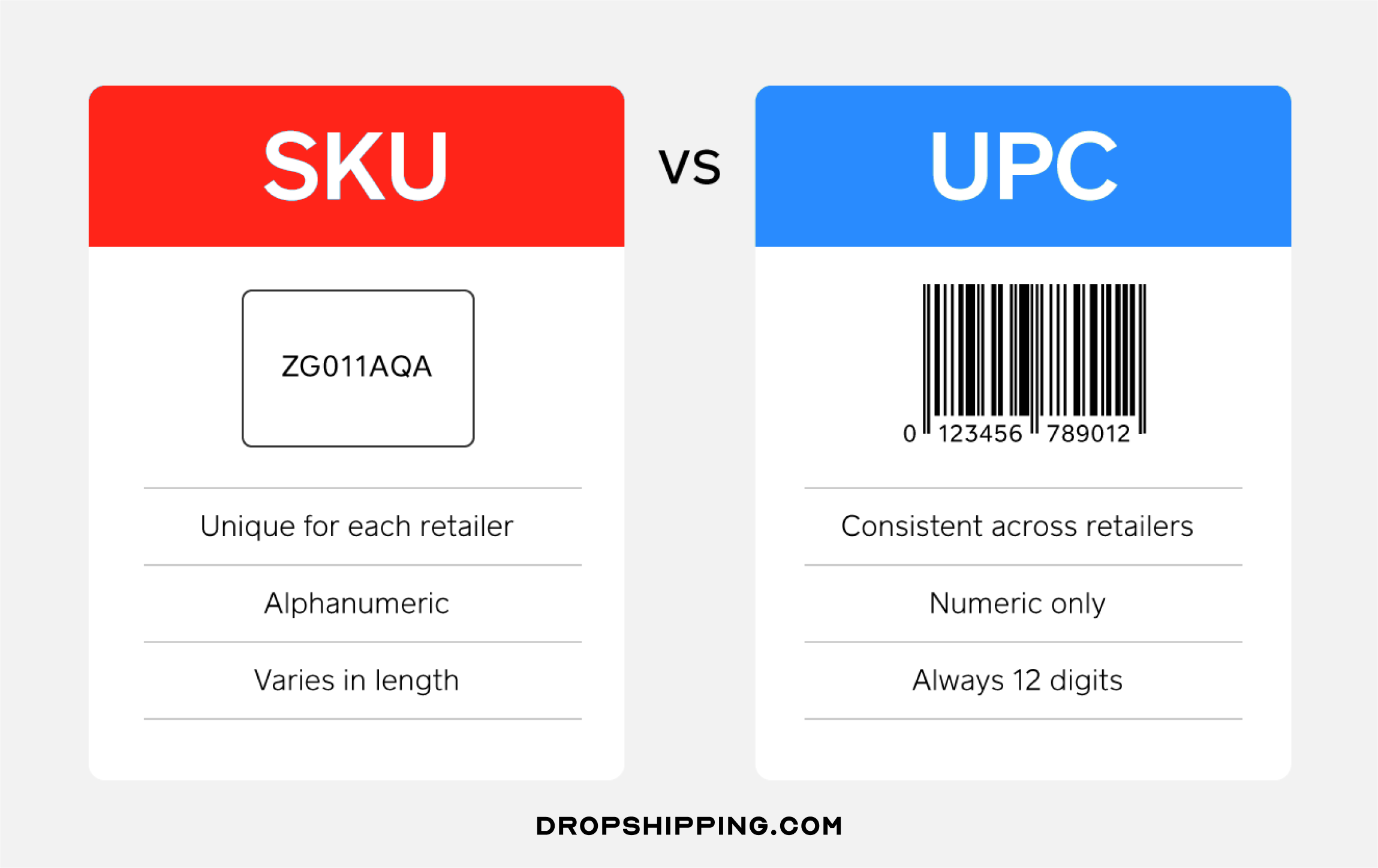
A common term that pops up alongside SKU is the Universal Product Code (UPC). While they may seem similar, there are noteworthy differences that set them apart.
So, let’s explain this difference in order to fully understand the SKU meaning. 👇
The UPC, often referred to as the UPC barcode or UPC code, is a unique 12-digit number assigned to retail merchandise that identifies both the product and the vendor selling it.
The primary function of a UPC is in retail scanning systems at the point of sale. Each time a product with a UPC code is scanned, information about that product is instantly pulled up from the system.
On the other hand, SKUs are unique identifiers set by individual businesses for internal use. They track not only products but also specific attributes like color, size, or manufacturer depending on how they’re structured.
While both UPCs and SKUs help keep inventory organized and managed effectively, their purposes and scopes differ.
🔸 Purpose
SKUs are primarily used for internal tracking and management of products within a single business’ operations. UPCs, meanwhile, are used by retailers to manage products from multiple vendors.
🔸 Scope
SKUs are unique to each business and can be customized based on the company’s needs. In contrast, UPCs are universal identifiers recognized across different retail platforms.
By understanding these distinctions between SKUs and UPCs, businesses can better leverage them in their sales and manufacturing processes for optimal efficiency.
Implementing an Effective SKU System in Your Sales and Manufacturing Processes
Upgrading your sales and manufacturing processes with a well-structured SKU system can be a game-changer.
It’s about understanding your unique business needs, creating a consistent SKU architecture, setting accurate reorder points, and utilizing inventory management systems to optimize your operations.
So, here’s a step-by-step guide to get you started:
Step 1: Understanding Your Business Needs for SKU Adoption
Before diving into SKU implementation, first, identify why your business needs it. For instance, consider an e-commerce store selling a wide range of products from different categories.
Using SKUs here can simplify inventory tracking and sales analysis.
Thus, by assigning unique SKUs to each product variant (size, color, etc.), you can quickly identify low-performing items or top sellers.
💡 Tip: Read about Dropshipping Business Plan – 13 Tips for Creating Yours.
Identifying Key Use Cases
If you’re operating a manufacturing facility, SKUs can help track components at different production stages. For example, a furniture manufacturer may use separate SKUs for raw materials, partially assembled items, and finished goods.
Step 2: Creating a Consistent and Scalable SKU Architecture
Consistency is vital when structuring your SKUs. Plus, is crucial to further understand the SKU meaning.
A well-planned SKU architecture makes it easier to categorize products and analyze sales data.
For instance, let’s say you run an online clothing store. Your SKU might look like this: MEN-SHIRT-RED-L, where the elements represent category, product type, color, and size respectively.
Or, if you have no idea how to create your SKU structure, there are numerous free tool online that can help you do that. For example, let’s try Zoho SKU generator. I will simply type im my product attributes.
The Role of Alphanumeric Codes and Category Identification
This alphanumeric structure helps distinguish between thousands of products while providing useful information at a glance.
Step 3: Setting Optimal Reorder Points through Data-Driven Approaches
Having efficient reorder points is crucial in preventing stockouts or overstocking scenarios.
By analyzing historical sales data and lead times with SKUs, you can set accurate reorder points. So, let’s get to this SKU meaning.
For instance, if a particular SKU often sells out within a week, you might set its reorder point to trigger when there’s a week’s worth of stock left.
Leveraging Technology
Inventory management systems can track sales trends and automatically adjust reorder points based on the SKU’s sales velocity.
This ensures you always have the right amount of stock, reducing holding costs and meeting customer demands effectively.
For example, I personally use Inventory Source for managing my inventory, tracking order, setting up SKUs, etc.
Let’s now explore how different industries use SKUs to optimize their processes.
Examples of Effective SKU Utilization in Different Industries
SKU codes are an essential part of many industries, and their usage varies based on the specific needs and characteristics of each sector.
So, here’s a look at how different industries use SKUs effectively, and how they explain SKU meaning.
Retail E-commerce Stores
E-commerce businesses often deal with a wide range of products. This variety requires a detailed system for tracking and managing inventory.
That’s where SKUs come in handy. Let’s take a hypothetical online bookstore as an example.
Categorizing Books
For books, an alphanumeric SKU like BK-HAR-001 can be used:
- ‘BK’ represents books
- ‘HAR’ signifies that it’s a hardcover
- ‘001’ is the unique identifier for the specific title
Managing Stationery Items
For stationery items such as pens, a SKU like ST-PEN-RED-01 can be used:
- ‘ST’ stands for stationery
- ‘PEN’ indicates the type of product
- ‘RED’ specifies the color
- ’01’ is the unique identifier
👉 Check out Dropshipping Books – How To Sell Books Without Inventory.
Manufacturing Industry
In manufacturing facilities, SKUs simplify the tracking of components and finished goods.
So, let’s imagine a furniture manufacturing unit using SKUs effectively.
Tracking Components
For example, a table leg may have an SKU like TL-MET-001:
- ‘TL’ represents table leg
- ‘MET’ indicates that it’s made of metal
- ‘001’ is the unique identifier
Managing Finished Goods
Similarly, a finished table may have an SKU like FT-MET-GLS-01:
- ‘FT’ stands for finished table
- ‘MET’ represents metal (material)
- ‘GLS’ signifies a glass top
- ’01’ is the unique identifier
By implementing effective SKU management systems like these, businesses can have better control over their inventory, leading to improved efficiency and reduced costs.
The Future of SKU Management: Leveraging Automation and AI
As we look ahead to the future of SKU management, there are two major trends that will revolutionize the industry: automation and artificial intelligence (AI).
Plus, its important in order to understand SKU meaning today.
Automation: Simplifying SKU Generation and Tracking
One of the key areas where automation is making a difference is in SKU generation and tracking. Traditionally, creating and managing SKUs has been a manual and time-consuming process. However, with the advent of automated systems, this is changing.
Automated SKU generation and tracking systems are becoming increasingly popular among businesses.
These tools leverage advanced algorithms to automatically create SKUs based on predefined parameters such as product type, color, size, and more.
They can also track the movement of products throughout the supply chain, providing real-time inventory data.
By implementing these automated systems, businesses can reduce manual errors, save time, and improve overall efficiency in their SKU management processes.
For example, OneCart is a free AI SKU generator that can help you generate listings of SKU’s in a minute. Also, the app helps you view and manage all your stock across all SKUs from every platform.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): Unlocking Insights and Efficiency
While automation is streamlining operations, AI takes SKU management to new heights by unlocking valuable insights and improving efficiency across various tasks.
✅ Predictive Analysis: Forecasting Future Demand
One area where AI can make a significant impact is in demand forecasting.
By analyzing large volumes of historical sales data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and trends that humans may miss.
This enables businesses to accurately predict future demand for different products and plan their inventory accordingly.
✅ Improved Customer Service: Access to Real-Time SKU Information
Another way in which AI can enhance SKU management is through improved customer service.
So, with AI-powered systems, customer service representatives can quickly access accurate and up-to-date information about specific SKUs.
This includes details such as product availability, shipping status, and estimated delivery times.
Thus, armed with this information, they can provide prompt and personalized assistance to customers, leading to higher satisfaction levels.
✅ Efficient Order Fulfillment: Speeding Up the Process
AI technology can also play a crucial role in optimizing order fulfillment operations.
So, by analyzing data from various sources, including SKU attributes, customer preferences, and warehouse layout, AI algorithms can identify the most efficient picking, packing, and shipping strategies for each order.
This not only helps to reduce processing times but also minimizes errors and improves overall productivity.
The Bright Future of SKU Management
With these advancements in technology, it’s clear that the future of SKU management is bright.
By leveraging automation and AI, businesses can streamline their operations, improve accuracy, and deliver better customer experiences.
But what’s next? In the next section, we’ll explore some practical tips and best practices for implementing these technologies effectively in your SKU management processes. So stay tuned!


Conclusion
Diving into the world of sales and manufacturing reveals the undeniable importance of SKU meaning. These unique identifiers are not just a random string of characters but the backbone of efficient inventory management and sales optimization.
By embracing SKUs, businesses unlock a realm of operational success, ensuring they can track their products with precision, forecast demand accurately, and fulfill orders with speed.
If you’re on the fence about integrating a robust SKU system, consider this a friendly nudge to take the leap. It’s not just about keeping up—it’s about staying ahead.
In today’s fast-paced market, those who wield SKUs effectively have a clear competitive edge. They can make informed decisions, reduce waste, and provide exceptional customer service.
Remember, each SKU is more than just an identifier; it’s a critical data point that informs every aspect of your operations from stocking shelves to shipping orders.
Harness its power in your sales and manufacturing processes, and you might just see your business transform in ways you never thought possible. Ready to start? Your future self—and your bottom line—will thank you for it.













![The Top 21 3PL Companies Compared [2024 List & Guide]](https://images.weserv.nl/?url=https://prod-dropshipping-s3.s3.fr-par.scw.cloud/2024/03/Frame-3922469.jpg&w=420&q=90&output=webp)